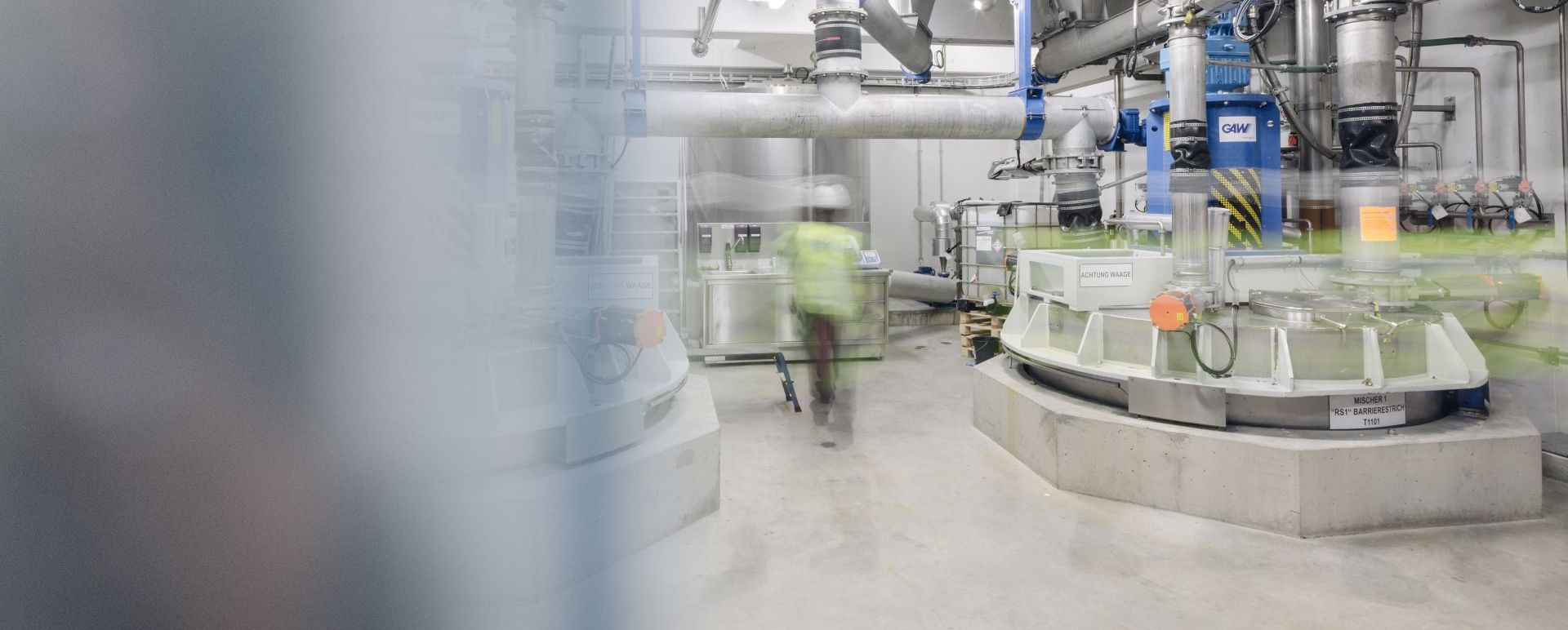
Step 1
Supply, Unloading and Storage

In the area of delivery, unloading and storage, media are pumped via a fine filter into the storage container. The delivery of the products is mostly by truck, railway wagon or container.
For over sixty years, GAW technologies has been engaged in the planning and turnkey construction of equipment for the handling and storage of products used in the manufacture and refining of paper and cardboard.
GAW technologies not only plans and delivers the unloading station, but also sets up the complete unloading system including all elements, as well as piping systems and automation.
The complete process of unloading is carried out in fully automatic operation. Only the hose needs to be manually connected to a fixed pipe. Operational safety, protection of personnel and the environment – these are our directives.
For this reason, GAW unloading stations are state-of-the-art and meet the highest safety requirements. Take the advantage of getting a system from a single source.
Automation
Step 2
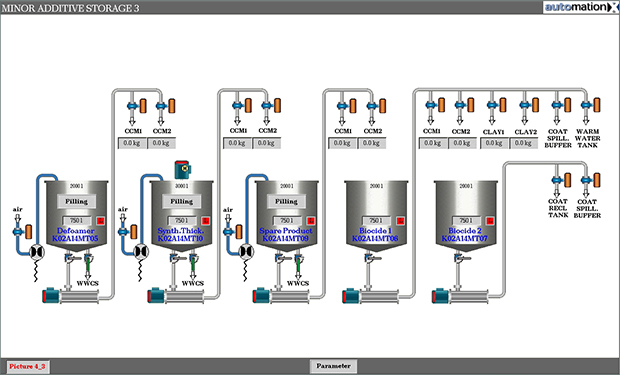
Additives Preparation

Paper and cardboard are mainly made from fibres and fillers.
In order to achieve the desired properties of the product, specific chemicals, so-called auxiliary substances, are also used. Auxiliary substances are also referred to as additives. They are either mixed directly into the paper stock or applied to the paper at certain points on the paper machine or by a coater. There is a difference here between paper additives and process chemicals.
Paper additives are components of the finished paper. They remain mainly in paper during production and serve to give the paper necessary or desirable properties. The paper additives include sizing agents, dry and wet strength agents, pigments, dyes, optical brighteners and coating binders.
Process chemicals in turn serve to control and improve the manufacturing process as well as keep the system clean. They usually only remain in the paper in traces. The process chemicals include, among others, retention and fixative agents, flocculants and slimicides as well as defoamers and deaerators. For an efficient production and coating process, the masterful preparation and exact dosage of the excipients are critical.
Automation
Step 3
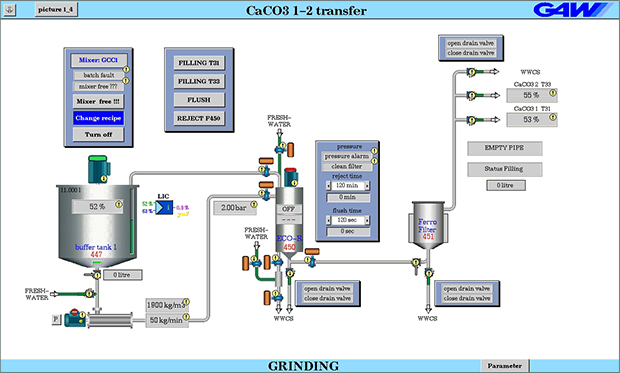
GCC Plant
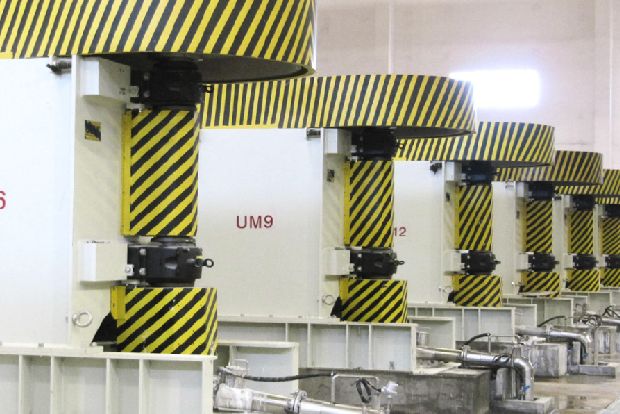

Ground calcium carbonate (GCC) is used in papermaking as a filler as well as a coating pigment for surface finishing, whereby the ultimate fineness of the final product is achieved only by single or multi-stage milling processes using GAW Ultramill technology.
With its unparalleled vertical design, the GAW Ultramill embodies an extension of horizontal grinding ball technology, enabling the preparation of customized particle sizes.
Since the successful launch of the GAW Ultramill in 1994, customers rave about the "excellent milling technology designed to make money".
To date, several hundred GAW Ultramills of various sizes have been installed worldwide for the dry and wet milling of calcium carbonate. The capacities of the individual systems range from 30,000 tons to 1,000,000 tons per year. It achieves levels of fineness of 60% ≤ 2 microns for filler, to 75% ≤ 2 microns for the precoat, and up to 90%, 95% and 98% ≤ 2 microns for the topcoat.
Automation
Step 4
Powder preparation
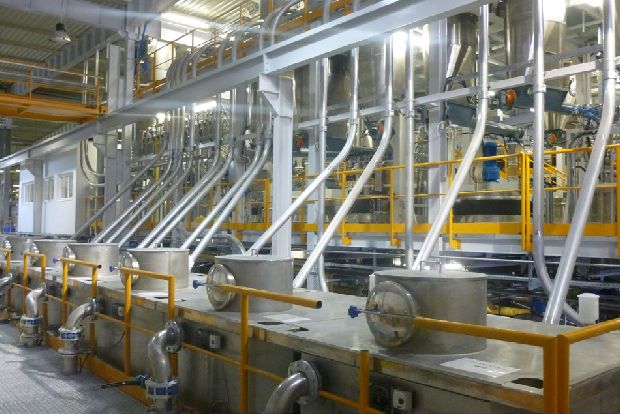

Pigments are colourants and are used in papermaking both as a filler and as a coating pigment.
The most important reason for adding filler to paper – in addition to the massive cost savings – is the improvement of the whiteness, brightness and covering capacity. Coating pigments usually consist of the same minerals as the fillers, differing from these essentially by the grain fineness.
The most common fillers and pigment minerals are ground calcium carbonate, kaolin, talc and titanium dioxide.
GAW technologies is a world-renowned specialist when it comes to total solutions for the storage, processing and dosing of these powder products, which must be handled with the utmost care.Automation

Step 5
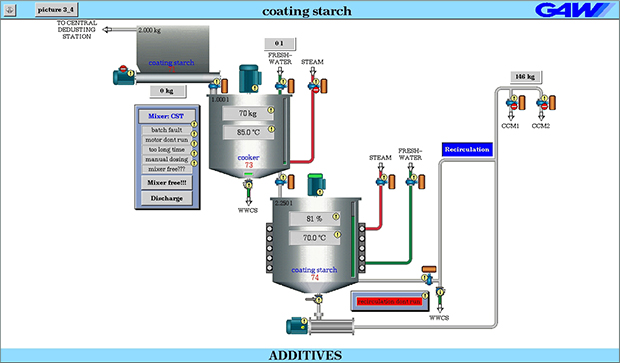
Starch preparation
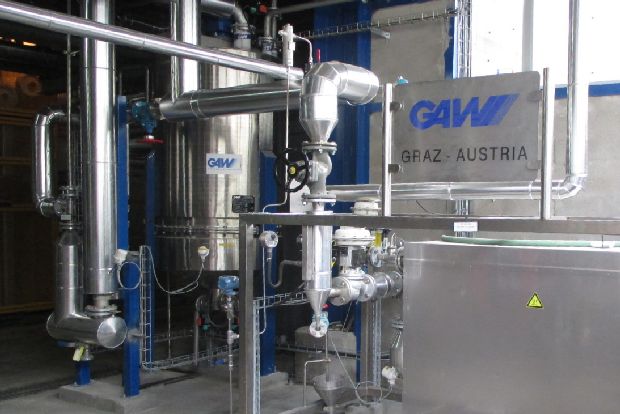

The history of starch in papermaking is as old as the printed word itself. Starch plays an important role in the various stages of the paper or cardboard manufacturing process, be it as an additive for internal sizing, surface sizing and finishing, or in the preparation of the coating.
The adequate cooking of the starch is an essential requirement for any application. The preparation of the starch includes all process steps, starting with the storage of the starch powder, to the dispersion, the gelatinisation and dilution for the intended purpose.
GAW technologies starch processing systems are either supplied as standardized "skid units" or tailored to the customer's special requirements.
In recent years, the patented GAW Heat Recovery System has been successfully installed in many starch processing systems. This system makes use of the heat energy that escapes during the cooking of starch, leading to a massive energy saving in the treatment.
Automation

Step 6
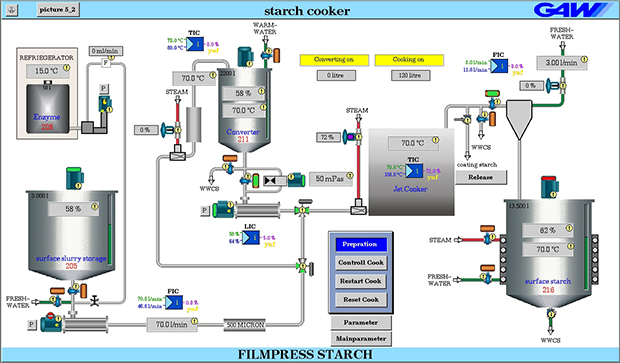
Heat Recovery System
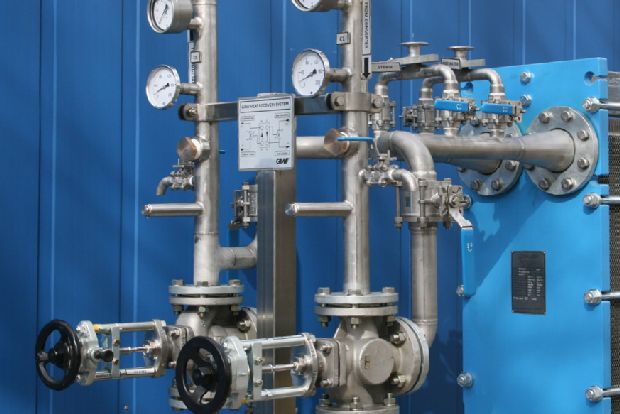

In the paper industry, cooking starch is a staple element regardless of the type of starch used. In this step, the starch is heated under pressure and by direct steam.
This is followed by relaxation in a cyclone, whereby the resulting expansion steam and heat energy contained therein escape unused into the atmosphere. Then the starch is stored.
In times of climate change and the accompanying climate agreements, we cannot allow ourselves to let this heat energy escape unused into the atmosphere. That's why GAW technologies has developed a compact modular system that recovers the energy through heat exchanger. The energy of the suspension is fed back in at the inlet to the boiler, thus reducing the amount of direct steam.
The patented GAW heat recovery system is well established in the market, enabling energy savings of over 50% for the inactivation of the jet boil.
Automation
Step 7
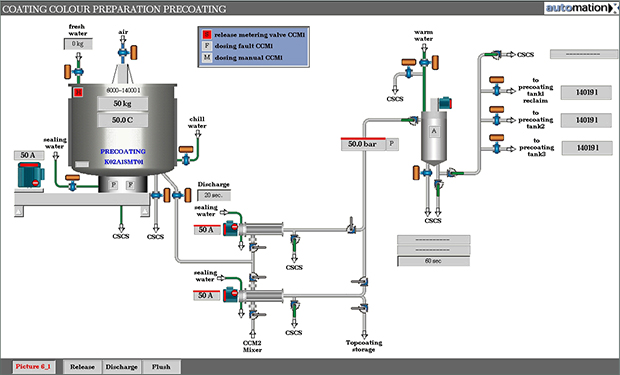
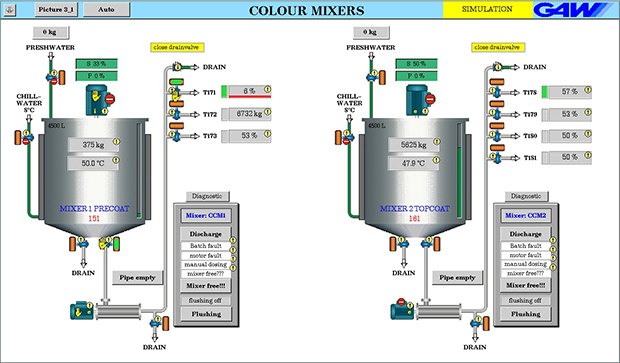
Dispersing machines
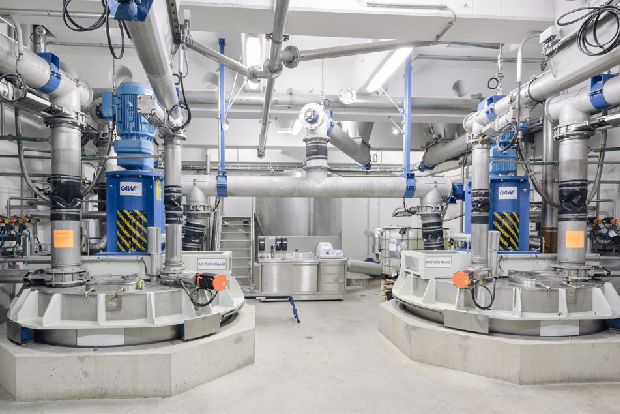

Dispersing, mixing and stirring are central and quality-determining steps in process engineering. The aim of these processes is to produce uniform and homogeneous mixtures of various raw materials as intermediates or final products. The ways to achieve this goal are as different as the properties of the raw materials and the final products.
GAW dispersing machines, the heart of every coating colour kitchen, are constructed under the premises of energy efficiency, consistent and reproducible qualities, scalability, preservation of the medium and optimum process connection. In decades of reliable partnerships with key customers, the processes and technology of the dispersing aggregates have been continuously improved and developed into highly efficient dispersing systems.
The focus is always on the goal of increasing the productivity and energy efficiency of our customers' plants, minimizing their operating costs and increasing environmental protection through the development of tailor-made customized technologies.
GAW dispersing machines, from simple dispersing discs to "Variable Shear Technology" dispersing units, are already used in various industrial sectors.
Automation
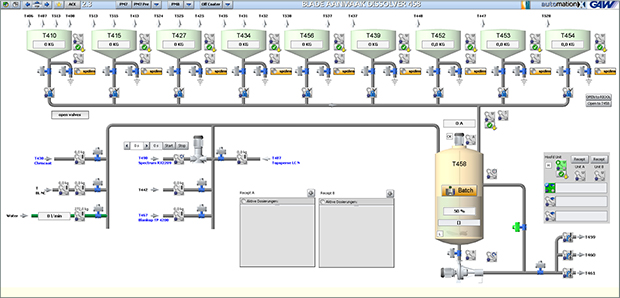
Step 08
Working Station
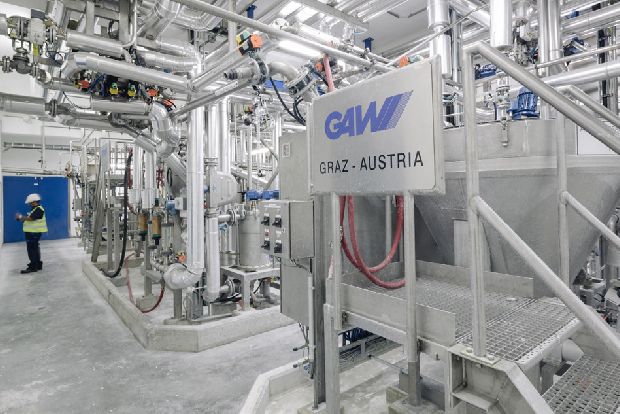

The Working Station is a circulatory system, via which homogenized coating colour, surface glue and other coating agents from the storage containers of the coating colour kitchen are pumped via filters into working containers. They are then pumped via further filters to the coating heads. Excess coating colour is returned to the working container after passing the coating unit via return lines.
In order to avoid disturbances in the line pattern (e.g. squeegee strips), GAW deaerators are used in addition to filter systems such as the ECO-R and ECO-S. The deaerators remove air and gas bubbles from the coating colour.
Depending on the design of the coating heads, the workstations are tailored to the application and adapted with quality control instruments. A big advantage of the GAW workstations lies in the unique piping, which minimizes the air content of the coating mass from the outset and prevents the build-up of agglomerates.
GAW has decades of experience in all of the established coating heads – hundreds of references from around the world make clear the excellence of our work.
Automation
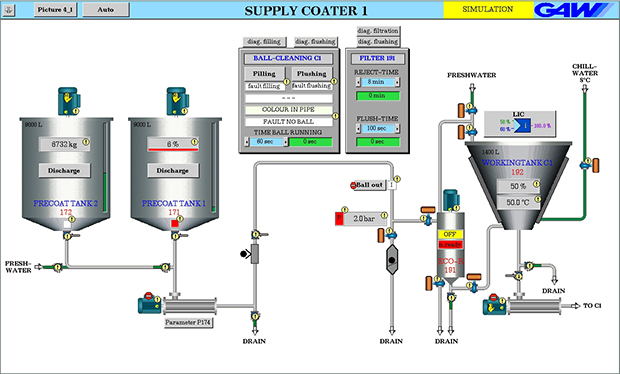
Step 9
Deaerators
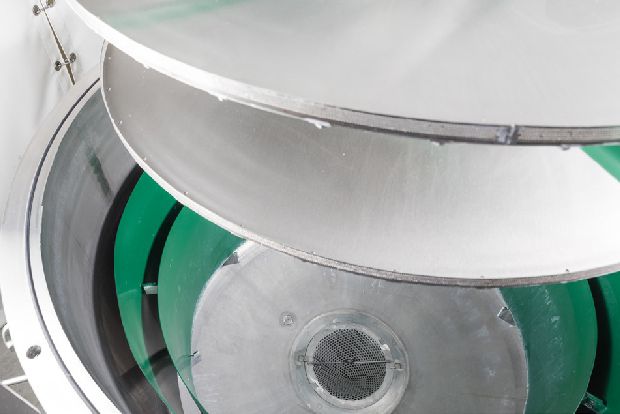

The first non-contact systems for applying coating colour and emulsions with a barrier effect on paper or cardboard had to be withdrawn from the market for a variety of reasons, but mainly due to the inefficient deaeration of the coating.
Special requirements for the coating materials for a curtain coater made it necessary to make further considerations with regard to coating colour properties and equipment requirements for coating colour bleeding. Here, the deaeration of coating colours turned out to be the essential process step in curtain coating, since air bubbles are not rubbed on paper or cardboard, but occur as imperfections in the form of oval-shaped, uncovered areas.
GAW deaerators are designed to reduce air in the coating colour to as much as 0.1%, depending on the coating colour properties and process parameters.
Automation

Step 10
Sodium dithionite solvent system
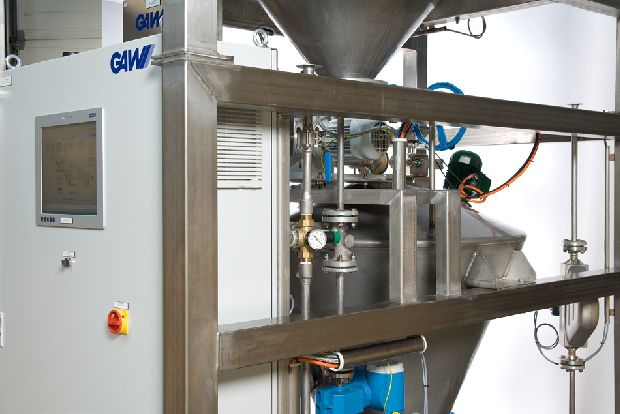

Sodium dithionite is a bleaching and reducing agent used primarily in the textile, paper and mineral industries.
Sodium dithionite makes it possible to replace a costly raw material like pulp with a less expensive one such as recovered paper. This saves money and is better for the environment. In addition, the reduction of contaminants protects the cellulose fibres.
GAW sodium dithionite solution systems are in use worldwide, providing excellent homogenization and mixing capabilities. The systems are compact, easy to start up and offer low maintenance costs.
Under the maxim of guaranteed operational safety, the GAW sodium dithionite solution systems ensure maximum performance and minimum product losses.
Automation

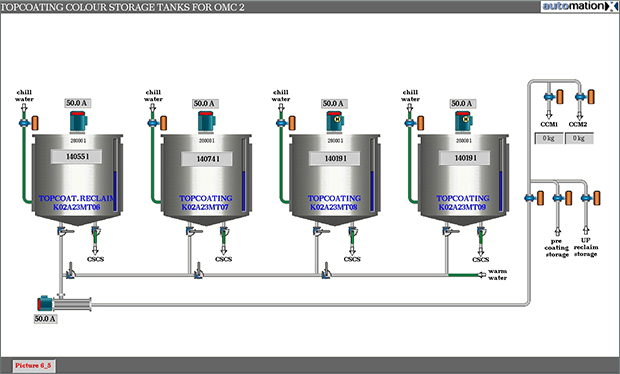
Step 11
Coating Colour Storage
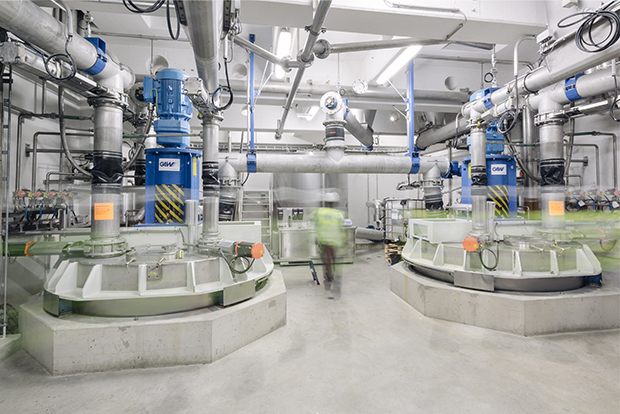

The dispersion is stored in coating colour storage tanks and gently agitated to avoid segregation and sedimentation.
Automation